Polishing Titanium: Titanium Polishing: Techniques & Applications
Updated : Feb. 7, 2025Titanium alloys are widely used in fields such as medical devices, aerospace, jewelry, and consumer electronics due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility.
To fully leverage these advantages, surface polishing becomes one of the key processes.

Why is polishing titanium important?
- Appearance: Polishing gives titanium a mirror-like shine, enhancing its natural beauty, making it especially suitable for consumer goods and jewelry that require high aesthetic standards.
- Protection: The polished surface provides additional protection, preventing minor scratches and wear.
- Enhanced corrosion resistance: While titanium is naturally corrosion-resistant, a polished surface reduces micro-gaps that could become potential sites for corrosion.
- Reduced friction: Polishing reduces surface roughness, minimizing friction to the greatest extent.
- Improved biocompatibility: In medical applications, polished titanium reduces surface irregularities, promoting tissue integration and minimizing inflammation.
- Food applications: Polished titanium surfaces are more hygienic and smoother, reducing the risk of bacterial growth.
- Electrical conductivity: Titanium has poor electrical conductivity, but polished titanium parts can significantly improve conductivity.
The scientific principle of polishing titanium
When the surface of titanium is rough or uneven, light scatters in multiple directions, causing the surface to appear matte or dull.
Polishing titanium alloys enhances the smoothness of the surface, allowing light to reflect evenly and create a bright shine.
After polishing, the titanium surface becomes smoother, resulting in more consistent light reflection and reduced light absorption, which brings out a high gloss and mirror-like effect.
This not only improves the aesthetic appeal of titanium products but also enhances their functionality and durability.
Challenges and solutions in titanium polishing
Titanium poses significant challenges in mechanical grinding and polishing due to its high chemical reactivity, low thermal conductivity, and high adhesion.
Ordinary abrasives are not suitable for polishing titanium, as they can easily cause surface grinding burns and microcracks.
Additionally, the speed of the polishing wheel should be controlled between 900 to 1800 meters per minute to ensure a gentle polishing process, avoiding overheating and surface damage.
Methods for mirror polishing titanium
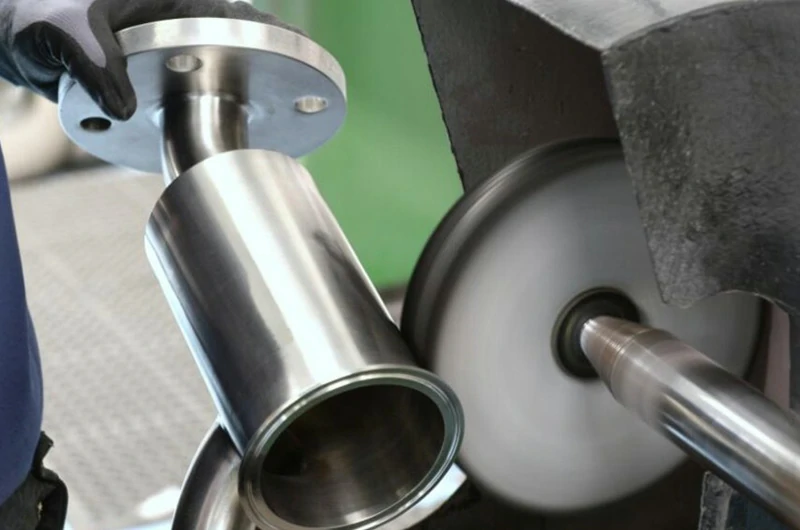
Mechanical polishing
The process begins with pre-treatment and progressive grinding to remove surface scratches and impurities. Coarse and medium polishing are then used to further eliminate grinding marks and enhance the gloss.
Finally, fine polishing is performed to achieve a high-brightness mirror-like effect.
The entire process requires the use of appropriate abrasives, polishing wax, and polishing wheels, while also paying attention to the direction and pressure of the grinding to ensure a uniform, smooth, and aesthetically pleasing titanium surface.

Chemical polishing
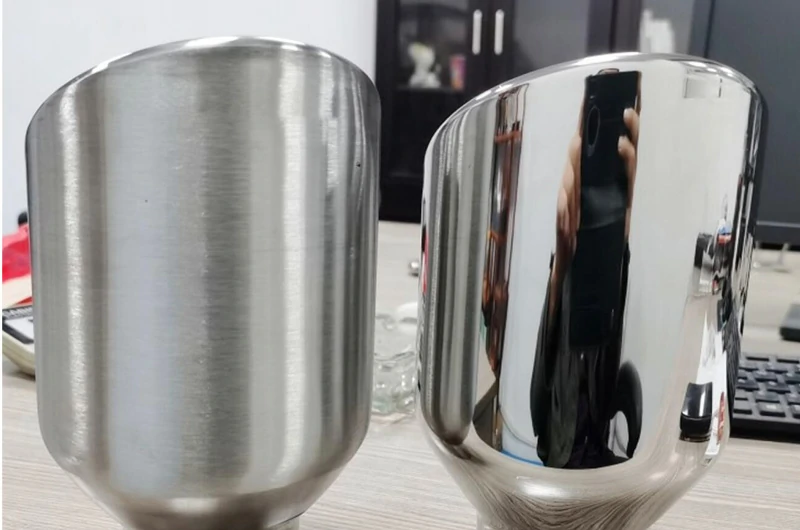
Chemical polishing is a process that uses chemical solutions to selectively dissolve the surface of a metal.
The raised areas of the surface dissolve faster, making the overall workpiece smoother and shinier.
For polishing complex structures, such as titanium alloy dental frameworks, chemical polishing does not require mechanical equipment, making the process relatively simple. The titanium workpiece is simply immersed in the polishing solution.
However, this method requires strict control of parameters such as temperature and time, as precision must be maintained to achieve the desired polishing quality.

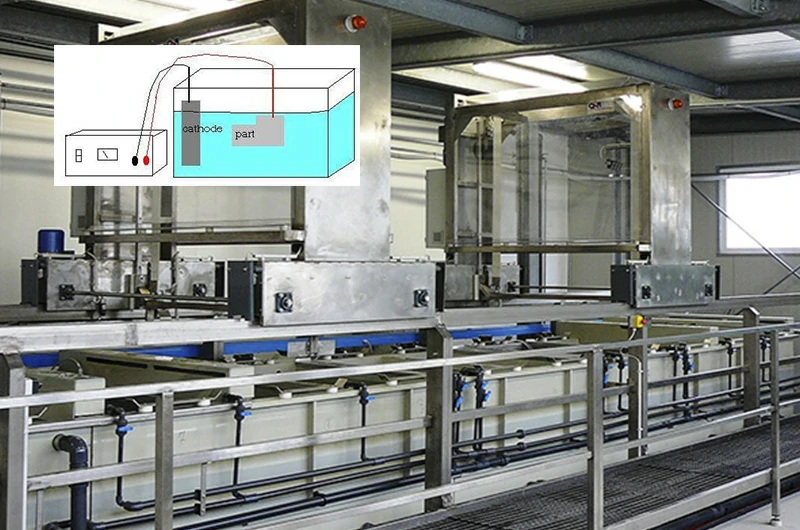
Electropolishing
Electropolishing is a process that uses electrochemical reactions to remove small protrusions from the metal surface, resulting in a smoother, shinier surface.
Compared to chemical polishing, electropolishing allows for more precise control over the amount removed, achieving a higher level of surface finish.
This method requires precise coordination of specific parameters such as electrolyte, voltage, current density, and temperature.
It can produce a uniform, stable, and high-quality surface in a short period and is widely used in industries with strict appearance and performance requirements, such as aerospace, medical devices, and high-end jewelry.

Ultrasonic polishing
Ultrasonic polishing uses ultrasonic vibrations to allow the abrasive slurry to perform fine grinding on the workpiece surface, removing surface defects and achieving high-precision polishing.
It features low macro forces, making it less likely to deform the workpiece, which is especially suitable for processing precision parts. However, it requires high precision in the manufacturing and installation of tooling.
Fluid polishing
Fluid polishing relies on the flowing liquid and its carried abrasives to scour the workpiece surface and achieve polishing.
Hydrodynamic grinding is driven by hydraulics, using a special compound (polymer-like substance) that flows well under low pressure and is mixed with abrasives such as silicon carbide powder.
Magnetic abrasive polishing
Magnetic abrasive polishing uses magnetic abrasives to form an abrasive brush under a magnetic field to efficiently and precisely grind the titanium workpiece surface.
This method can achieve micron-level smoothness and is especially suitable for the precise processing of titanium tubes used in aerospace applications.
Electrical discharge ultrasonic composite polishing
Electrical discharge ultrasonic composite polishing combines the effects of ultrasonic vibration and high-frequency pulsed currents.
Both ultrasonic vibration and electrical pulses work simultaneously on the workpiece surface, rapidly reducing surface roughness.
Titanium alloy polishing process flow
The titanium alloy polishing process involves several key steps to ensure the final product has a smooth, flawless surface with excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Below is a detailed process flow:
- Surface pre-treatment: Before polishing, the titanium alloy surface must be thoroughly cleaned to remove rust, oxide layers, grease, and other contaminants, laying a solid foundation for the subsequent processes.
- Grinding (coarse polishing): During the grinding stage, surface defects and irregularities are removed to ensure the titanium alloy surface is flat.
- Mirror polishing: The polishing stage further enhances the surface smoothness through mechanical or chemical methods, achieving a mirror-like finish.
- Cleaning: The workpiece is thoroughly cleaned with water or appropriate cleaning agents to remove any residual polishing compounds and abrasives, ensuring the surface is clean and free from moisture.
- Surface treatment: Depending on the specific requirements and applications, surface treatments such as electroplating or anodizing are applied to improve corrosion resistance and decorative qualities.
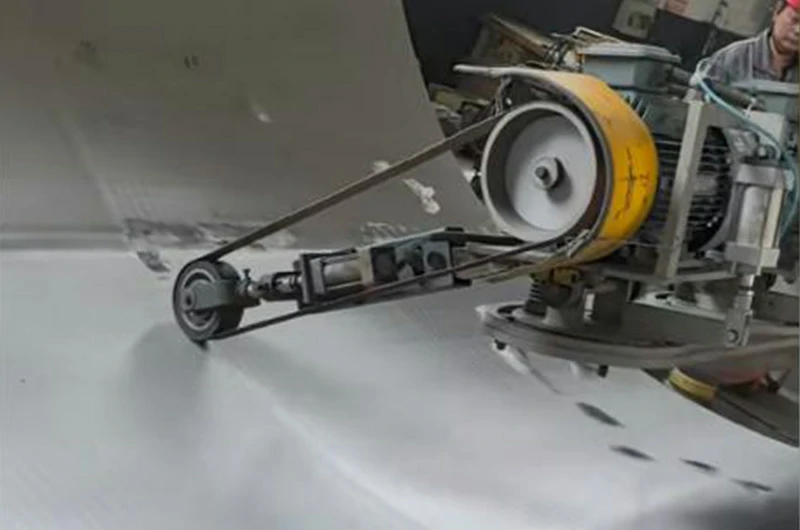

How to easily polish titanium products at home?
Safety precautions
Wear safety goggles, protective gloves, and a mask if necessary to prevent debris from causing injury.
Initial cleaning
Wash the titanium surface with warm water and a neutral detergent to remove grease. For stubborn oil stains, use acetone or alcohol.
Progressive sanding
Start with coarse sandpaper (such as 220 grit) and gradually move to finer grits (800, 1000, 2000 grit). Use water or a lubricant while sanding to prevent overheating.
Each time you switch to a finer grit, ensure that the previous sanding marks are completely removed.
Polishing
Use a polishing machine or an electric drill with a cotton or wool buffing wheel, along with a polishing compound suitable for titanium or stainless steel.
Intermittently cool the surface to prevent discoloration or surface damage from high temperatures.
Final cleaning and inspection
Remove any leftover polishing compound and wipe the surface clean with a soft cloth. Check the smoothness and gloss level.
Titanium polishing case studies: from medical to everyday applications
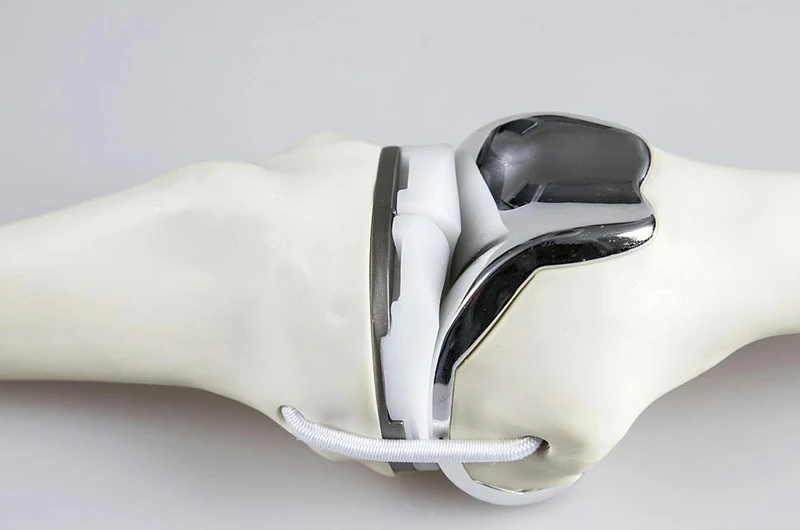
Titanium alloy artificial joint polishing
By improving the surface smoothness of titanium joints, friction and wear are reduced, while ensuring dimensional and shape accuracy to prevent negative impacts on joint function. We use industrial robots combined with force/position control systems for polishing.
This system can monitor and compensate for grinding status in real-time, adapting to deviations in different shapes with millisecond-level response. The servo motor precisely adjusts the grinding force, ensuring an even polishing process with consistent material removal.
How to polish and clean titanium jewelry
Restoring the shine of titanium jewelry at home is quite simple. First, soak the jewelry in a solution of mild soap and baking soda, and leave it for a few hours to remove dirt and grease.
Next, use a household brush to gently scrub the surface. After cleaning, rinse thoroughly with water and dry with a clean towel.
To achieve a mirror-like polish, it is recommended to use a nylon pad and a polishing compound suitable for titanium, gently polishing the surface, and finally wiping with a lint-free cloth.
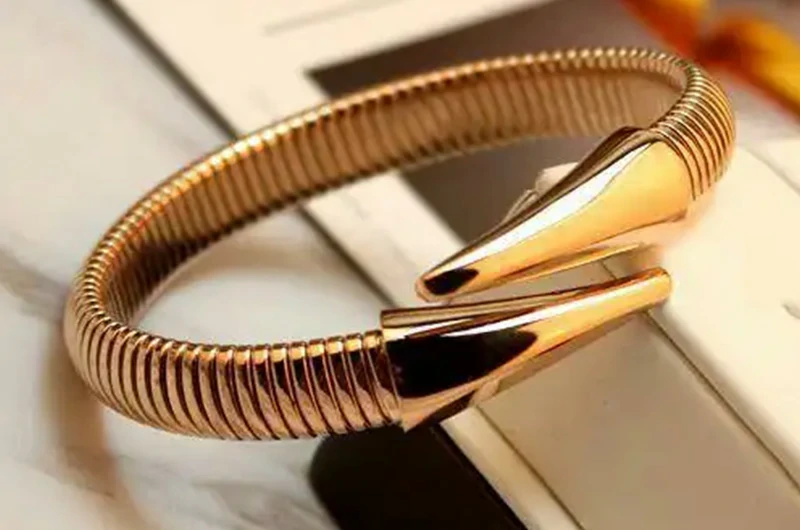

How to polish a titanium metal watch strap?
To polish a titanium metal watch strap at home, first remove the strap and soak it in a solution of soap and baking soda in water for several hours. Use an ultrasonic cleaner or a soft-bristled brush to gently scrub away dust and dirt.
Then, rinse thoroughly with clean water and dry with a clean towel. Next, apply a special titanium diamond wax or polishing paste, and gently polish for a few minutes with a nylon microfiber cloth until the surface regains its mirror-like shine.
How to polish the inner surface of titanium alloy elbow tubes
Polishing the inner surface of titanium alloy elbow tubes requires extremely high precision and meticulous process control.
Using polymer elastic soft abrasives in an extrusion motion, the inner wall of the tube is precisely ground.
This method not only improves the polishing effect, making the inner wall as smooth as a mirror, but also effectively reduces production costs. Each polishing step is carefully controlled in terms of process parameters to ensure the accuracy of the workpiece’s dimensions and shape.


How to polish titanium rods?
First, use a regular diamond abrasive rubber wheel for fine grinding, gently removing burrs and unevenness from the surface, avoiding overheating and surface damage.
Next, use the barrel polishing method, placing the titanium rod, abrasives, water, and additives into a rotating and vibrating barrel polisher.
Through continuous friction between the abrasives and the titanium rod, the surface is uniformly polished without worrying about dust contamination or high labor intensity.

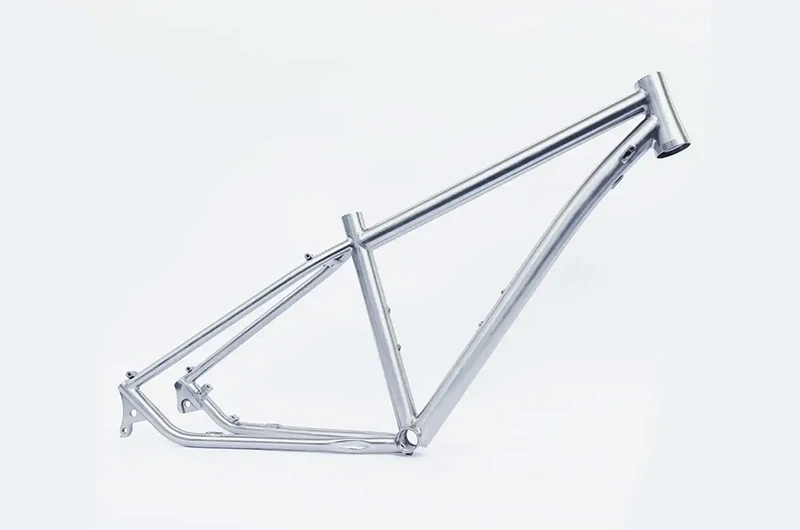
How to polish a titanium alloy bicycle frame?
Clean the frame thoroughly, gently wipe it with soap to remove dirt and dust, avoiding abrasive tools like steel wool to prevent scratches.
Next, apply a special titanium diamond wax or polishing paste, and use a nylon microfiber cloth to gently buff the frame surface, continuing for several minutes until the mirror-like shine is restored.
After polishing, use a clean cloth to completely remove any residual paste or wax, and perform a final cleaning and drying.

Other surface treatment options for titanium alloys?
In addition to titanium polishing, manufacturers use the following processes to achieve the desired surface finish for parts.
- Anodizing: An electrochemical process forms a titanium oxide layer, enhancing corrosion resistance and durability, but it may affect thermal conductivity.
- Plating: A metal coating (such as nickel) is applied to the titanium surface to improve wear resistance and corrosion resistance, but it is time-consuming and may pose potential environmental hazards.
- Brushing: A polishing brush is used to smooth out surface imperfections, leaving a matte finish, but it may reduce corrosion resistance and is more costly.
- Powder coating: Plastic powder is applied to the titanium surface to provide a tough and durable coating, but it is expensive and may degrade under UV exposure.
Common titanium polishing questions: tips and care
Polishing tips for titanium
Before performing surface finishing on titanium, ensure it is properly cleaned. Start with coarse sandpaper and gradually move to medium and fine sandpapers, followed by surface refinishing with materials like nylon or other fine fibers.
Avoid using sharp steel wool or dirty cloths, as these may cause surface scratches and roughness.
How often should I clean titanium items?
The cleaning frequency depends on how frequently the item is used. Items that are frequently handled, such as titanium jewelry, should be polished regularly to maintain their shine.
Items that are occasionally used or stored in controlled environments may not require frequent polishing. If the item shows signs of wear or scratches, polishing can be considered.
Can I polish a titanium ring at home?
Yes, you can polish a titanium ring at home using the appropriate materials and techniques.
Soft cloths and gentle polishing agents can remove light scratches and maintain the shine. For deeper scratches or specific effects, professional polishing may be more suitable.
Does polishing weaken the performance of titanium?
When done correctly, polishing does not weaken the performance of titanium. It only enhances the surface.
Over-polishing or improper polishing may damage the natural oxide layer of titanium, affecting its performance. Using the correct technique can prevent over-polishing.
What are the signs that titanium has been over-polished?
Over-polishing may result in an uneven surface or even deformation of the material. The protective oxide layer of titanium may be removed, making it more susceptible to corrosion.
The fine details and complex designs of titanium components may also be lost. If these signs appear, polishing should be stopped to prevent further damage.
Can polishing create a mirror finish on titanium alloy parts?
Yes, titanium surfaces can achieve a mirror finish through polishing. With the right polishing agents and techniques, titanium can become highly shiny, enhancing both its aesthetic appeal and functionality.
Are there any limitations to titanium polishing?
Not all titanium parts are suitable for polishing, especially those subjected to extreme temperatures or high stress. For parts that are already corroded or damaged, polishing may not restore their performance and other repair methods may be needed.