Titanium Anodizing
Updated : Feb. 19, 2025Titanium anodizing is an electrochemical surface treatment process widely used to enhance the corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetic appearance of titanium products.
This technology not only improves the performance of titanium components but also provides a range of vibrant decorative colors, making it widely applied in industries such as aerospace and medical equipment.
What is titanium anodizing?
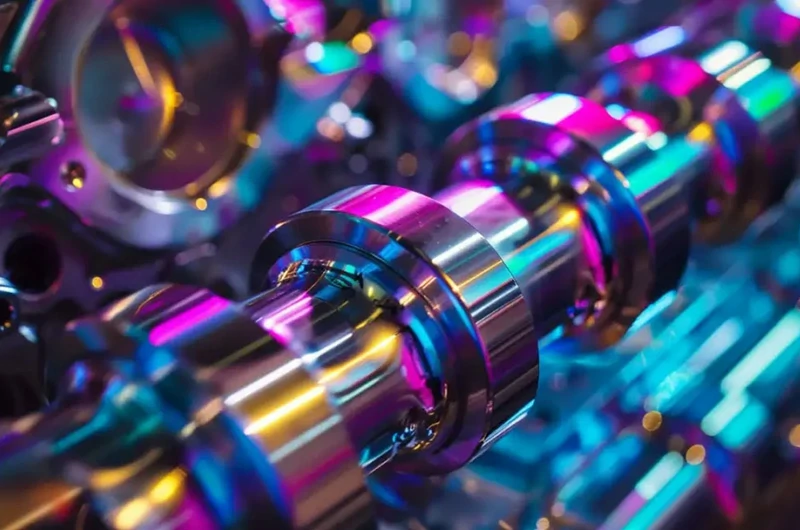
Titanium anodizing is a process that thickens the natural oxide layer on the surface of titanium, enhancing its corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and appearance. The process involves immersing titanium components in an electrolyte solution and applying direct current to form a durable oxide film, with the color effect adjustable based on the voltage applied.

Steps of titanium anodizing:
Cleaning and pre-treatment
First, the titanium parts must be thoroughly cleaned. This process involves immersing the titanium components in an alkaline solution to remove dirt, grease, and oxide residue from the surface. Cleaning is crucial because any remaining contaminants will affect the effectiveness of the anodizing process. After cleaning, the parts need to be rinsed in deionized water to completely remove any remaining cleaning agents.
Setup of anodizing equipment
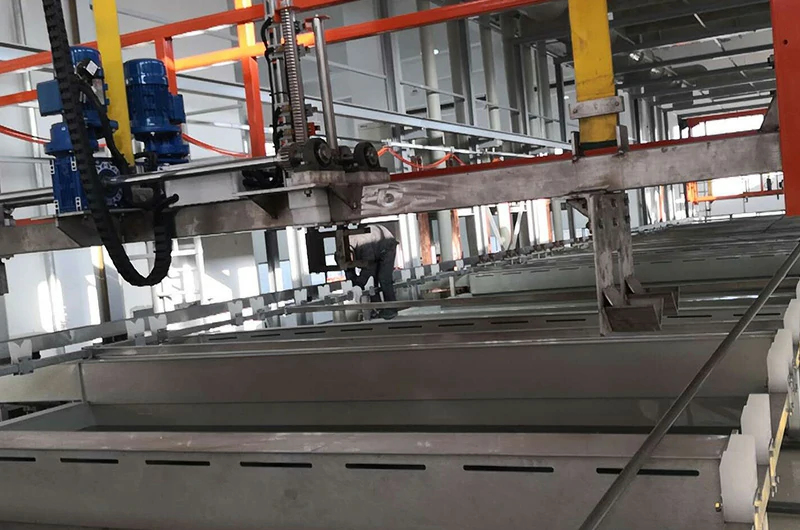
Next, the cleaned titanium parts are placed into the anodizing equipment and connected to the positive terminal of the power supply, making them the anode in the electrochemical reaction.
Electrolytic process
Once the titanium parts are connected as the anode, they are immersed in an electrolyte solution, typically a weak acid such as sulfuric or phosphoric acid. The electrolyte's role is to conduct the current and drive the electrochemical reaction, resulting in anodizing.

Control of voltage, current, and temperature
The thickness of the oxide layer and the final color effect depend on the voltage, current, and temperature used during the anodizing process. Higher voltage results in a thicker oxide layer, and the color will change accordingly. Precise control of these parameters is crucial to achieving the desired results, so this step requires high precision.
Post-treatment
After anodizing is complete, the titanium parts are thoroughly rinsed to remove any remaining electrolyte. In certain applications, a sealing process may be required, where the titanium components are immersed in boiling water to close the pores in the oxide layer, thereby enhancing their corrosion resistance.
Advantages of titanium anodizing
- Reduces the risk of part wear by decreasing friction and increasing hardness.
- Enhances the corrosion resistance of the anodized (passivated) surface.
- Biocompatibility, creating a low-corrosion and zero-pollution surface.
- Low cost and long-lasting color.
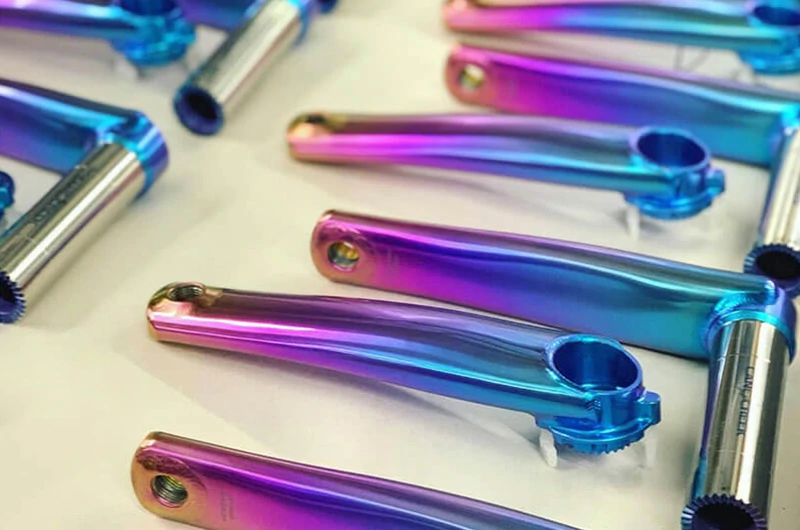
- High aesthetic quality with a wide range of color options.
- Electro-passivation and low-corrosion surface.
- Biocompatibility recognition, as no dyes or colorants are used.

Limitations of titanium anodizing
Although titanium anodizing offers many advantages, it also has some limitations:
- Cost: Due to the materials and equipment required, the anodizing process can be expensive.
- Limited thickness: The anodized layer has a maximum thickness, which may not be suitable for all applications.
- Color consistency: Achieving uniform color is difficult because variations in the anodizing process can lead to different shades.
- Not suitable for all titanium alloys: Some titanium alloys may not anodize well, limiting their use in certain applications.
Applications of titanium anodizing
Aerospace: Titanium anodizing is widely used in components such as hydraulic systems, fasteners, and casings due to its excellent corrosion resistance and lightweight properties, extending service life and improving fuel efficiency.
Medical: Due to its biocompatibility and resistance to bodily fluids, anodized titanium is commonly used in implants, surgical instruments, and valves, offering resistance to in-body corrosion and maintaining sterility.
Automotive: With high strength and low weight, anodized titanium is often used to manufacture components like connecting rods that require both strength and weight reduction. It also improves heat resistance and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for parts such as exhaust systems.
Consumer Goods: Anodized titanium is popular in products like watches, eyeglasses, frames, and sports equipment due to its aesthetic appeal and durability. It provides color and luster while protecting items from wear and environmental impact.
Industrial: Anodized titanium is widely used in heat exchangers and reaction vessels due to its corrosion and heat resistance, capable of withstanding high temperatures and effectively transferring heat while being resistant to corrosion.
Standards and specifications for titanium anodizing
When anodizing titanium, adhering to specific standards ensures that the process meets quality, safety, and performance requirements. These standards cover the anodizing process, material usage, and the quality of the final titanium components.
International standards
ISO 7599:2018: This standard specifies the requirements for anodic oxidation coatings of aluminum and its alloys. Although it primarily targets aluminum, certain parts of it are also applicable to titanium anodizing, especially regarding surface treatment and testing methods.
- Key Requirements: Includes pre-treatment, coating application, and quality control.
- Testing Procedures: Involves testing for coating thickness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
- Surface Characteristics: Specifies requirements for uniformity of the oxide film and color consistency.
U.S. standards
ASTM B892-14: Specifically for anodic oxide coatings on titanium and titanium alloys, focusing on evaluating characteristics such as the adhesion, thickness, and durability of the oxide layer.
- Adhesion Testing: Evaluates the adhesion of the oxide film to the titanium surface.
- Thickness Measurement: Provides standards for measuring the thickness of the oxide layer.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Ensures that titanium parts remain protected in corrosive environments.
- Applications: Suitable for aerospace components that require high corrosion resistance and durability.
- Coating Characteristics: Specifies requirements for coating thickness, color, and adhesion.
- Process Guidelines: Provides detailed instructions for the anodizing process to ensure proper treatment of titanium components.
Industry-specific standards
Aerospace Standards: Titanium anodizing is critical in the aerospace industry for improving component durability and corrosion resistance, ensuring performance and safety under extreme conditions.
- AMS 2488C: Ensures that aerospace components meet sufficient corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
- ASTM B600: Specifies cleaning and descaling methods for titanium parts before anodizing.
Medical Device Standards: Due to its biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, titanium anodizing is widely used in the medical industry, especially for implants and surgical instruments.
- ISO 10993: Assesses the biocompatibility of medical devices, ensuring that anodized titanium is safe and harmless when used in the human body.
- ASTM F86: Specifies surface treatment requirements for titanium in biomedical applications, ensuring anodized titanium promotes bone integration and reduces rejection risk.

What are the types of anodizing?
There are three main types of titanium anodizing: Type I, Type II, and Type III. The commonly used types are Type II and Type III. Type I is less common and is used for specialized high-temperature treatments.
Type 1 titanium anodizing
One of the main advantages of Type 1 anodizing is its ability to enhance the metal's high-temperature resistance.
During the anodizing process, a thin and uniform oxide layer forms on the surface of the titanium. This oxide layer acts as a protective barrier, shielding the underlying metal from corrosion and oxidation. What makes Type 1 anodizing unique is that it maintains this protective barrier even when exposed to high temperatures.
Type 2 titanium anodizing – wear resistance and corrosion resistance
Type 2 titanium anodizing primarily enhances wear resistance and corrosion resistance by forming a thick oxide layer on the titanium surface. This process uses a lower voltage (typically 15 to 30 volts) to create a colorless, transparent oxide film, improving the durability and abrasion resistance of the titanium.
Titanium with Type 2 anodizing typically has the following advantages:
- Excellent wear resistance: The thick oxide layer provides outstanding wear resistance, making it suitable for high-stress environments.
- Enhanced corrosion resistance: Ideal for harsh environments, especially performing excellently in aerospace and medical industries.
- Maintained natural appearance: The transparent oxide layer does not alter the natural color of the titanium, preserving its original aesthetic appeal.
Common applications of type 2 titanium anodizing:
Aerospace components
Titanium implants
Industrial applications with high durability requirements
Type 3 titanium anodizing – color effects and aesthetics
Type 3 anodizing, also known as color anodizing, creates various vibrant colors by adjusting the voltage (typically in the range of 50 to 120 volts), resulting in oxide films of different thicknesses. In addition to its aesthetic appeal, Type 3 anodized titanium still retains a certain level of corrosion resistance and durability.
Advantages of type 3 anodized titanium:
- Wide range of colors: Offers a variety of colors to meet customization and branding needs.
- Visually appealing: Ideal for applications where visual impact is important, enhancing the product's appearance.
- Flexible customization: Color coding and unique visual effects add value to the product.
Common applications of type 3 anodized titanium:
- Decorative items and jewelry
- Consumer electronics
- Other products requiring color and visual appeal
Differences between type 1, 2, 3 titanium anodizing
| Properties | Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Low | High | Highest |
| Thickness ranges | 0.5 to 2.5 Micrometer | 2.5 to 25 Micrometer | 25 to 100 Micrometer |
| Corrosion resistance | Good | Better | Best |
| Hardness | Low | High | Highest |
| Abrasion resistance | Low | High | Highest |
| Colour intensity | Dull | Dull | Vibrant |
| Colour | Dull silver | Gray | Green, blue, violet, purple, golden |
| Purpose | Commercial | Functional + aesthetics | Aesthetic + functional |
| Uniformity | Less | More | Most |
| Commercial names | Chromic acid anodizing | Sulfuric acid anodizing | Hard coat anodizing |
| Application | Improve adhesion of coatings and paints | Improve corrosion resistance, wear resistance | Improves corrosion resistance, wear resistance and mechanical properties |
What colors are available for anodized titanium?
Titanium anodizing exhibits a rich range of colors without the need for dyes or pigments by controlling the thickness of the oxide layer. The voltage adjustment determines the thickness of the oxide film, which in turn affects light interference and produces different colors. Available colors include gold, blue, purple, green, pink, and many other shades, with the color variation directly related to the voltage level.
This is a basic titanium color chart showing voltage levels and corresponding colors:

| Voltage (V) | 15 | 30 | 50 | 80 | 90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Brown | Blue | Yellow | Purple | Green |
| Film Thickness(nm) | 300 | 500 | 700 | 950 | 1300 |
What anodized titanium products can Chalco provide?
Chalco offers a variety of anodized titanium products, including titanium plates, tubes, rods, and wires, with diverse color, thickness, and surface treatment options available based on customer requirements.
These products are widely used in aerospace, medical devices, architectural decoration, and consumer goods, combining aesthetics and functionality to meet the demands for corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and high strength across various industries.

Anodized titanium tube

Anodized titanium bar

Anodized titanium plate