Does Titanium Have Magnetic Properties?
Updated : Feb. 19, 2025Titanium is a common metal because it is strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant. Although titanium has many ideal properties, a common question is whether titanium has magnetic properties.
What is magnetism?
Magnetism is a natural fundamental force caused by the movement of charges. It largely depends on the electron structure, particularly the unpaired electrons in its outermost shell.
The spins of these unpaired electrons can align in response to an external magnetic field, resulting in paramagnetism or ferromagnetism.
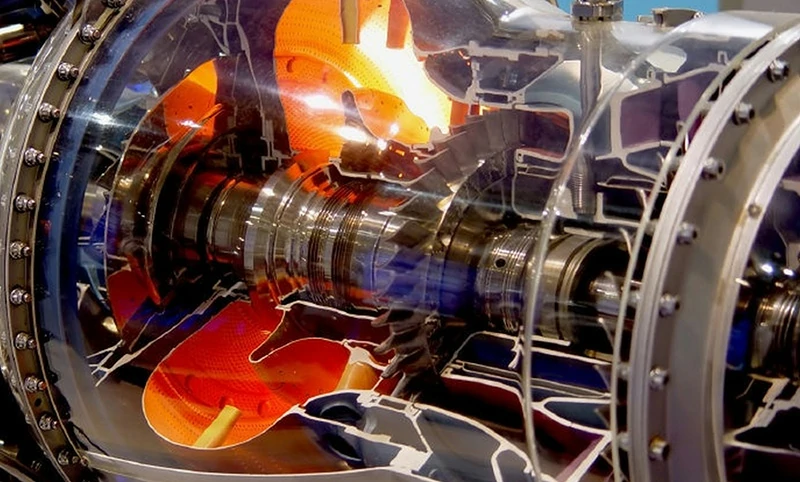
Does titanium have magnetic properties?
The simple answer is no, titanium usually does not have magnetic properties.
This is because its crystal structure is highly ordered and it lacks unpaired electrons. For a material to exhibit magnetism, it must have unpaired electrons.
The influence of titanium's electron structure
Every metal atom has electrons, and the movement and spin (direction of rotation) of these electrons generate magnetism. Unpaired electrons can produce magnetism, but titanium's electrons exist in pairs.
The spin directions of these paired electrons are opposite, canceling out the magnetic effect. As a result, titanium itself does not produce a magnetic moment and therefore does not have magnetic properties.
The reason behind titanium's crystal structure
Titanium's atoms are arranged very closely and regularly in its crystal structure. This highly ordered arrangement means that even if there are weak magnetic moments, they cannot align properly to form an overall magnetic property.
Factors affecting titanium's magnetic properties
Interestingly, if we change certain parameters, titanium's magnetic behavior can also change, and vice versa. But what are these factors? Let's take a closer look!
Pressure
High pressure can disrupt titanium's crystal structure, causing its atoms to arrange irregularly.
When this happens, small magnetic moments may align, causing titanium to exhibit weak magnetic properties. However, this magnetism is temporary and very weak.
It is important to note that this magnetic behavior only occurs under extremely high pressure.
Temperature
- At room temperature: Titanium is non-magnetic.
- At low temperatures: As the temperature drops, the thermal energy inside titanium decreases, making it easier for electrons to align with an external magnetic field, resulting in weak magnetism.
- At high temperatures: As the temperature rises, thermal disturbances disrupt the alignment of titanium's magnetic moments, further weakening its magnetic behavior.
Alloying elements
Pure titanium is non-magnetic. However, the magnetism of titanium alloys can vary depending on the alloying elements.
- If the alloying elements are strongly magnetic (such as iron or nickel), the titanium alloy may exhibit some magnetic properties and could even be attracted to magnets.
- If the alloying elements are non-magnetic (such as aluminum or vanadium), the titanium alloy generally retains titanium's non-magnetic characteristics.
Magnetic field strength
Titanium's response to an external magnetic field is proportional to the magnetic field strength.
- In weak magnetic fields, titanium's paramagnetism is almost undetectable.
- In strong magnetic fields, titanium will show a more noticeable paramagnetic response, but this magnetic reaction is still very weak.
Common titanium alloys and their magnetism
Ti-6Al-4V (Titanium Alloy Grade 5)
Composition: Titanium (90%), Aluminum (6%), Vanadium (4%)
Magnetism: One of the most commonly used titanium alloys, frequently applied in aerospace and medical fields. Like pure titanium, Ti-6Al-4V alloy is non-magnetic.

Ti-5Al-2.5Sn
Composition: Ti-92%, Al-5%, Sn-2.5%
This alloy is commonly used in marine applications and has a similar weak magnetic response.
Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo
Composition: Ti-82%, Al-6%, Sn-2%, Zr-4%, Mo-6%
Known for its high strength and corrosion resistance, this alloy's magnetism is similar to other titanium alloys.
Titanium-Nickel Alloy (Shape Memory Alloy)
Titanium-nickel alloys are famous for their excellent memory effect and superelasticity.
Composition: Titanium and Nickel
Magnetism: Titanium-nickel alloys exhibit slight paramagnetism, but the overall magnetic response remains very weak.
Titanium-Iron Alloy
Composition: Titanium and Iron
Magnetism: Titanium-iron alloys are typically used to strengthen the steel industry or to manufacture wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials. Their magnetism increases with the iron content.
Titanium-Cobalt Alloy
Titanium-cobalt alloys are commonly used in high-temperature, wear-resistant scenarios.
Composition: Titanium and Cobalt
Magnetism: Cobalt is a ferromagnetic element, and when alloyed with titanium, it may enhance the material's magnetism. However, titanium still predominates, so the overall magnetism remains weak.
Non-magnetic properties of titanium and Its application fields
Medical applications
Medical implants: Dental implants, bone plates, joint replacements, spinal correction devices, etc.
Surgical tools: Non-magnetic surgical tools and precision instruments.
MRI machine housings and components.
Aerospace applications
Titanium is lightweight yet strong, making it ideal for manufacturing aircraft components, such as engine housings and fuselage parts. Its non-magnetic properties help protect sensitive avionics equipment.
Electronics and engineering
Titanium’s non-magnetic properties are crucial for manufacturing enclosures for electronic devices used in magnetically sensitive environments, such as precision navigation systems.
Military bomb disposal robots
Titanium’s non-magnetic nature means it is unaffected by strong magnetic fields, making it suitable as a material for bomb disposal robots.
Power generation equipment
Titanium’s non-magnetic properties, combined with its high temperature and corrosion resistance, make it ideal for manufacturing turbine blades and heat exchangers in the power generation industry.
Titanium surface treatment and magnetic properties analysis
As we mentioned earlier, pure titanium is always non-magnetic. It does not exhibit any attraction to magnets.
Now, let's practically test the magnetism of titanium after surface treatment. The method of verification is to connect a magnet and see if it is attracted.
Pure titanium
Pure titanium is non-magnetic, so the magnet cannot attract it at all.

Anodized pure titanium
Anodized pure titanium is also non-magnetic, so the magnet will not be attracted at all.

Pure titanium PVD
Pure titanium PVD is also non-magnetic, so the magnet will not stick at all.

Does titanium's non-magnetism affect its CNC machining?
Challenges in fixturing
In CNC machining, securing the workpiece is crucial to ensuring machining accuracy.
Impact: Magnetic fixtures cannot be used to secure titanium workpieces, which may increase setup time and complexity.
Solution: Mechanical fixtures, vacuum fixtures, or custom fixtures are needed to secure titanium workpieces.
Considerations for chip removal
During CNC machining of titanium, a significant amount of metal chips is generated.
Impact: Due to titanium's non-magnetism, magnetic chip collectors are ineffective at gathering titanium chips.
Solution:
- Manual cleaning: Operators need to regularly clean the chips manually.
- Non-magnetic collection system: Using vacuum cleaners or airflow systems to automatically remove chips.
Machining efficiency and costs
Due to the above challenges, CNC machining of titanium may require more time and resources, which could affect machining efficiency and increase costs.
Comparison of magnetic properties of common metals

Colored steel sheet
Common colored steel sheet. It is magnetic, so magnets can stick to it perfectly.

Galvanized steel sheet
Common galvanized sheet metal. Galvanized steel sheet is magnetic, so magnets can stick to it perfectly.

General stainless steel SUS304 (austenitic)
General stainless steel is non-magnetic, so magnets cannot attract it. However, bending and other processing may cause certain areas to become magnetic.

Ferritic stainless steel
A typical example is SUS430. SUS430 is magnetic, so magnets will stick to it.

Aluminum
Aluminum is non-magnetic, so magnets cannot stick to it.

Copper
Copper sheets are non-magnetic, so magnets cannot attract them.
Common questions about titanium's magnetism
Is titanium safe for MRI?
Yes, titanium is safe in MRI because it is non-magnetic. It does not interact with the magnetic fields generated by MRI systems.
Can titanium be magnetized?
No, titanium cannot be magnetized and does not retain magnetism.
Is titanium paramagnetic or ferromagnetic?
Titanium is paramagnetic. Its electron structure, with four unpaired electrons, is paramagnetic because paramagnetism depends on unpaired electrons.
Does titanium jewelry have magnetism?
No, titanium jewelry is non-magnetic. Titanium metal is inherently non-magnetic, so it does not attract magnets and does not have any magnetic field.
Can metal detectors detect titanium?
Titanium does not trigger traditional metal detectors because it does not contain enough ferrous material (such as iron or nickel).
Is titanium stronger than steel?
Titanium is generally a strong and durable metal with excellent corrosion resistance.
However, whether it is stronger than steel depends on its type and alloy. Its lightweight property makes it ideal for the aerospace industry.
Is titanium conductive?
Yes, titanium is conductive, but not as much as copper or aluminum. While its conductivity is not as good as other metals, it still allows current to pass through.
This makes it useful in certain electrical applications where high conductivity is not as important, but corrosion resistance is needed.