10 Properties of Titanium Metal
Updated : Feb. 7, 2025Titanium is a silver-white transition metal with the chemical symbol Ti and an atomic number of 22. it is one of the most abundant elements on earth, primarily found in minerals such as rutile and ilmenite.

Due to its excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature resistance, and biocompatibility, titanium plays a crucial role in various fields. from aerospace to medical applications, from marine engineering to high-end consumer products, titanium meets diverse and demanding requirements with its unique properties. next, we will delve into the top 10 characteristics of titanium to understand its significance in modern technology and industry.
High strength and low density
Titanium has high strength, primarily attributed to its crystal structure (hexagonal close-packed structure). This structure effectively disperses stress under force, preventing material deformation. At the same time, titanium atoms are relatively light, with a density about 57% that of steel, meaning its mass per unit volume is smaller.
Typical applications: Used in aircraft frames, wing spars, engine components, and titanium alloy bicycle frames, offering both weight reduction and sufficient strength support.

Low thermal conductivity
Titanium has low thermal conductivity, only about 1/5 that of steel, 1/13 that of aluminum, and 1/25 that of copper. This is mainly due to its hexagonal close-packed crystal structure and lower free electron density, which limit the efficiency of heat conduction.
Typical applications: In aircraft and spacecraft, titanium is often used in components that require thermal insulation, such as fuselage and engine parts.
Corrosion resistance
Titanium has excellent corrosion resistance, with a dense oxide film formed on its surface that effectively protects the titanium substrate from corrosion. Titanium is highly stable in oxidative, neutral, and mildly reducing environments, and can withstand corrosion from air, seawater, and most acid and alkaline solutions. However, it is sensitive to highly corrosive substances such as hydrofluoric acid, concentrated hydrochloric acid, and concentrated sulfuric acid. Titanium also has self-healing properties, as the oxide film rapidly regenerates after wear.
Titanium or titanium alloy.:Ti grade 1, Ti grade 2, Ti-0.2Pd, Grade 7 (Ti-0.2Pd), Ti-3Al-2.5V.
Typical applications: chemical reaction vessels, marine equipment, underwater transportation pipelines.
High-temperature resistance
Titanium can maintain high strength and creep resistance in high-temperature environments, primarily due to its high melting point (1668°C) and excellent high-temperature structural stability. The high-temperature performance of titanium depends on the alloying elements in titanium alloys, such as aluminum and molybdenum, which help maintain crystal structure stability at high temperatures, preventing deformation caused by thermal stress.
Typical alloys: Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo-0.1Si, Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo, Ti-5Al-4Cr-4Mo-2Sn-2Zr.
Typical applications: Engine components for aerospace, rocket combustion chambers, high-temperature heat exchangers, and more.

Low-temperature resistance
Some titanium alloys actually experience an increase in strength at low temperatures, with only a slight reduction in plasticity, primarily due to their hexagonal close-packed crystal structure. This structure maintains its plasticity and toughness at -255°C, unlike many metals that become brittle. This characteristic allows titanium to retain stable mechanical properties even in extreme low-temperature environments.
Typical alloys: Ti-5Al-2.5Sn ELI, Ti-6Al-4V ELI.
Typical applications: Deep-sea detectors, cryogenic containers for liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen rocket engines, or manned spacecraft.
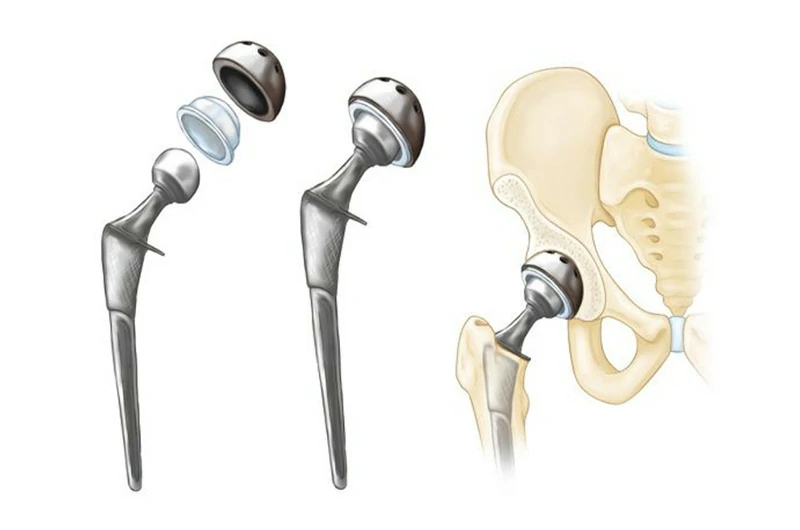
Biocompatibility
Titanium has excellent biocompatibility, allowing it to be compatible with human tissue without triggering rejection reactions. The titanium oxide film on its surface creates a similar chemical environment to the calcium, phosphorus, and other components found in human tissue, which is the reason for titanium's biocompatibility.
Typical alloys: Ti-6Al-7Nb, Ti Grade 1, Ti Grade 2, Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Grade 23).
Typical applications: Artificial hip joints, knee joints, shoulder joints, rib joints, skull bones, heart valves, and skeletal fixation clips.
Non-magnetic
Titanium is a non-magnetic metal, meaning it is unaffected by magnetic fields. This is due to its electronic structure, which lacks magnetic properties. The outer electron configuration of titanium does not meet the conditions required to generate magnetism, resulting in an extremely weak or nonexistent response to external magnetic fields.
Typical applications: Titanium is often used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipment to avoid interference with magnetic fields and in high-precision devices where magnetic stability must be maintained.
Strong damping resistance
Titanium has excellent damping resistance, primarily due to its hexagonal close-packed crystal structure, low internal friction factor, and superior elasticity and plasticity, which effectively absorb and attenuate vibrational energy.
Typical applications: Used in structural components of aircraft and spacecraft, such as wings, engine parts, and nozzles, to reduce vibration and noise and enhance flight stability.

Radiation resistance
Titanium metal has excellent absorption of ionizing radiation, effectively shielding against radiation. Its lattice structure and relatively high density allow it to absorb significant radiation energy, reducing the impact on the surrounding environment.
Typical applications: Radiation protection in nuclear reactors, shielding materials in nuclear waste storage facilities, and protective equipment in high-radiation environments.
Tensile strength is close to its yield strength
This property of titanium, reflected in its high yield strength ratio (tensile strength/yield strength), indicates that titanium has limited plastic deformation capability during forming. Due to the high ratio of titanium's yield limit to its elastic modulus, it exhibits significant springback during forming.
Titanium properties reference table
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic number | 22 |
| Atomic weight | 47.9 |
| Atomic volume | 10.6 W/D |
| Covalent radius | 1.32 Å |
| Ionization potential | 6.8282 V |
| Thermal neutron absorption cross section | 5.6 barns/atom |
| Color | Dark gray |
| Density | 4.51 g/cm³ (0.163 lb/in³) |
| Melting point | 1668 ± 10 °C (3035 °F) |
| Solidus/liquidus | 1725 °C (3135 °F) |
| Boiling point | 3260 °C (5900 °F) |
| Specific heat (at 25 °C) | 0.5223 kJ/kg K |
| Thermal conductivity | 11.4 W/m K |
| Heat of fusion | 440 kJ/kg (estimated) |
| Heat of vaporization | 9.83 MJ/kg |
| Specific gravity | 4.5 |
| Hardness | 70 to 74 HRB |
| Tensile strength | 240 MPa (35 ksi) min |
| Young’s modulus | 120 GPa (17 × 10⁶ psi) |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.361 |
| Coefficient of linear thermal expansion | 8.41 µm/m K |
| Electrical conductivity | 3% IACS (where copper = 100% IACS) |
| Electrical resistivity (at 20 °C) | Not provided |
| Electronegativity | 1.5 Pauling’s |
| Temperature coefficient of electrical resistance | 0.0026/°C |
| Magnetic susceptibility (volume, at room temperature) | 180 ( ±1.7) × 10⁻⁶ mks |
What products and services can Chalco provide for you?
As a globally renowned supplier of metal materials, Chalco also holds a significant position in the field of titanium products and related services. We are committed to providing comprehensive titanium solutions to our customers, whether it is from material supply to processing services, or from technical support to customized needs. Chalco can be your trusted partner.
Titanium product categories
- Titanium bar: Available in various specifications and alloy types, meeting the demands for high strength and corrosion resistance in aerospace, medical, chemical, and marine engineering fields.
- Titanium plates: Suitable for shipbuilding, chemical equipment, and architectural decoration. We can process and customize according to customer requirements.
- Titanium tubes: Used in heat exchangers, medical implants, and the energy industry, offering excellent oxidation resistance and high-temperature performance.
- Titanium wires: Ideal for welding, high-precision component manufacturing, and other applications, with multiple surface treatment options available.
Typical applications of products
Chalco's titanium products and services are widely used in the following fields:
- Aerospace: Manufacturing lightweight, high-strength aerospace components.
- Medical field: Titanium orthopedic implants and medical devices.
- Chemical and marine engineering: Corrosion-resistant equipment manufacturing.
- Energy industry: Heat exchanger tubing, nuclear power equipment parts.
Processing services
- Precision cutting: Using high-precision equipment to ensure the shape and dimensions of the material meet customer requirements.
- Surface treatment: Includes sandblasting, polishing, and oxidation treatment to enhance the durability and appearance of titanium products.
- Custom processing: Tailoring titanium alloy products according to the specific needs of different industries and applications.
Technical support
- Material selection advice: Recommending the most suitable titanium alloy types based on different usage scenarios and budgets.
- Processing guidance: Providing technical guidance on titanium material processing, welding, and assembly to optimize usage efficiency.
- Industry standard consulting: Ensuring titanium products meet international quality standards such as ASTM and AMS, offering customers high-quality assurance.