Application of Titanium in the Maritime Industry

Still troubled by frequent maintenance and high operating costs of traditional ships? Still searching for a revolutionary material that truly enhances ship performance and extends service life?
Now, titanium is transforming the industry with its exceptional corrosion resistance, ultra-lightweight properties, and extended durability. It brings unprecedented performance improvements and long-term value to your vessels.
The emergence of marine-grade titanium is set to revolutionize your expectations!
Specifications of marine-grade titanium
Standards: ASTM B265, ASTM B338, ASTM B348, ASTM B363, ASTM B367, ASTM B381, ASTM B600, ASTM B861, ASTM B862, ASTM B863
Classification Society Certifications: ABS, DNV GL, LR, BV, RINA, KR
International Certifications: ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001
Material Compliance Certificate: Each batch of titanium comes with a certificate of conformity, ensuring it meets specific chemical composition and physical performance requirements.
What titanium alloys are used in ships?
- Grade 2: The most commonly used titanium alloy in ships. It offers excellent ductility and is widely applied in ship components, heat exchangers, and marine fasteners. It also provides outstanding crevice corrosion resistance in seawater applications up to 180°F (82°C).
- Grade 5: Ti-6Al-4V is a versatile titanium alloy with higher strength and good corrosion resistance. It is ideal for critical marine applications such as propellers, shafts, and subsea exploration equipment.
- Grade 7: For superior crevice corrosion resistance at temperatures exceeding 500°F (260°C), Grade 7 titanium is the preferred choice.
- Grade 9: Ti-3Al-2.5V offers a balance of strength, formability, and corrosion resistance, making it commonly used in piping for marine and offshore structures.
- Grade 12: This titanium alloy contains palladium to enhance corrosion resistance. It is typically used in heat exchangers and other components exposed to highly corrosive marine environments.
Applications of titanium in ships
Titanium and titanium alloys are widely used in the maritime industry. Key applications include hull structures, propulsion systems, heat exchangers, coolers, piping systems, valves, pumps, propellers, and sonar devices.
Pumps, valves, piping, and fittings in ships
Titanium piping is widely used in ships, primarily for seawater transport, condensation systems, fuel delivery, and drainage systems.
Thanks to its excellent corrosion resistance, erosion resistance, and low density, titanium alloys enable the production of thin-walled, small-diameter pipes and fittings.
This not only significantly reduces weight but also provides a lifespan far superior to copper or stainless steel products.
Piping in ship systems
Titanium pipes excel in seawater environments due to their exceptional corrosion resistance and pressure resistance.
Contact us now

Titanium pipe fittings
Titanium pipe fittings in ships offer outstanding corrosion resistance, strength, and lightweight advantages.
Contact us nowHeat exchangers, condensers, coolers, and evaporators
Heat exchangers, condensers, coolers, and evaporators made from titanium are highly durable and resistant to high-speed corrosive seawater. They offer a maintenance-free lifespan of over 100,000 hours without requiring zinc anode protection.
Titanium shell-and-tube heat exchanger
Made from Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy, these heat exchangers utilize superplastic forming and diffusion bonding technology, significantly saving space and weight.
Contact us now

Titanium spiral heat exchanger
Titanium spiral heat exchangers are corrosion-resistant, efficient, and lightweight, helping to reduce maintenance costs.
Contact us nowSteam engine
Titanium alloy steam engines are widely used in the power systems of Russia’s existing nuclear-powered icebreakers. The use of titanium alloys extends their service life by more than ten times.
Contact us now

Titanium condenser

Titanium cooler

Titanium evaporator
Ship propulsion system
Compared to copper alloys and steel, titanium alloy propellers have a lifespan more than five times that of copper alloy propellers. Due to their low density, titanium propellers not only reduce ship weight but also enhance speed and fuel efficiency.
Propellers
Titanium alloy propellers offer high strength, lightweight properties, and excellent cavitation and fatigue resistance.
Contact us now

Propulsion shafts and couplings
These components operate in seawater for extended periods. Titanium effectively prevents corrosion, significantly extending their service life.
Contact us nowAcoustic devices
Acoustic devices on ships can also be made from titanium alloys. Applications include sonar domes, underwater acoustic transducer components, microphones, and telephone parts.
Titanium alloy sonar domes offer excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and superior acoustic transparency.
Contact us now
With outstanding overall performance, titanium sonar domes have been used in the sonar systems of Russian naval vessels such as Kursk, Minsk, and Kiev.
Hull structural components
Hull and bulkheads
Titanium effectively resists saltwater corrosion, making it suitable for outer hulls and inner bulkheads of ship cabins.
Contact us now

Bottom plates
With high strength and corrosion resistance, titanium is an ideal choice for the bottom of ship cabins.
Contact us nowStern and bow structures
In specialized stern and bow structures, titanium alloys provide high strength to withstand seawater erosion.
Contact us now
All-titanium alloy ships
In some cases, entire ships are built from titanium alloys. All-titanium ships are lightweight, fast, fuel-efficient, and have exceptionally low maintenance costs.

Racing speedboats

Hand-rowed titanium boats

Titanium fishing boats
Japan’s first registered titanium speedboat measures 12.25 meters in length, 4.06 meters in width, and 2.25 meters in depth. It was manufactured by Nissei Industry Co. and launched in August 1997.
The entire speedboat used approximately 1.7 tons of titanium. The rudder, rudder shaft, and propeller shaft were all made from Ti-6Al-4V alloy.
Pressure-resistant hulls
In the naval industry, titanium alloy pressure-resistant hulls are primarily used in deep-sea submersibles and submarines.
With high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and non-magnetic properties, titanium is an ideal material for deep-sea pressure hulls.
Russia was the first country to use titanium alloy pressure hulls in nuclear submarines. Six Typhoon-class nuclear submarines were constructed using industrial pure titanium, Ti-6Al-4V (Ti64), Ti-6Al-4V ELI, Ti-6Al-2Nb-1Ta-0.8Mo, Ti-3Al-2.5V, IIT-3B, IIT-7M, and other alloys, with a total titanium usage of up to 9,000 tons.
Submarine pressure-resistant hulls
Submarines utilize a double-layer titanium hull structure, offering advantages such as higher speed, lower noise, and reduced maintenance frequency.
Deep-sea submersible pressure-resistant hulls
Another critical application of titanium pressure-resistant hulls is in deep-sea submersibles.
Submarine pressure-resistant hulls
Submarines utilize a double-layer titanium hull structure, offering advantages such as higher speed, lower noise, and reduced maintenance frequency.
Contact us now
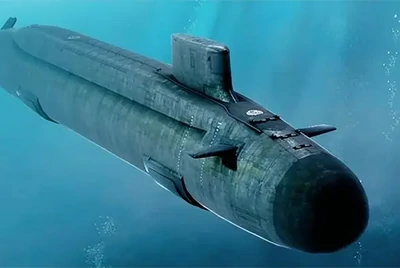
Deep-sea submersible pressure-resistant hulls
Another critical application of titanium pressure-resistant hulls is in deep-sea submersibles.
Contact us nowThe United States, Japan, and France have successively used titanium and titanium alloys for pressure hulls. The Ti-6Al-2Nb-1Ta-0.8Mo alloy was used in the hulls of the U.S. Alvin and Sea Cliff submersibles.
Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy was applied in the buoyancy spheres of the French SM97, the U.S. Alvin, the Japanese Shinkai 2000, and in the hulls and buoyancy spheres of the U.S. Navy's Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicle (DSRV).
Ship whip antennas
Whip antennas on ships utilize titanium alloys for their strength, corrosion resistance, and non-magnetic properties, ensuring reliability and durability in harsh marine environments.
Titanium alloys help maintain antenna performance while reducing weight and extending service life.
Contact us now
Common titanium alloy grades and their applications in ships
| Application areas | Titanium alloys |
|---|---|
| Pressure-resistant hulls | Ti-5Al-2.5Sn, Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-2Nb-1Ta-0.8Mo, Ti-6Al-4V ELI |
| Propellers and propeller shafts | Pure titanium, Ti-6Al-4V |
| Seawater pipelines, valves, and fittings | Pure titanium, Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-Al-Mn, Ti-6Al-6V-0.5Cu-0.5Fe, Ti-3Al-2.5V, Ti-Ni shape memory alloy, Ti-31, Ti-75 |
| Heat exchangers and seawater desalination systems | Pure titanium, Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-Al-Mn, Ti-5Al, Ti-0.3Mo-0.8Ni, Ti-31 |
| Engine components | Ti-5Al-2.5Sn, Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-8Al-1Mo-1V, Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo |
| Acoustic devices | Pure titanium |
| Mooring and launching systems | Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-4Al-0.005B |
Popular titanium alloy products in the shipbuilding industry
We offer customized titanium solutions for marine applications, tailoring special specifications and grades to meet customer requirements.
Whether for hull structures, propellers, piping systems, or other critical components, we provide tailored solutions to ensure optimal performance and durability.Quick Quote
Titanium pipes for marine applications
Titanium pipes are lightweight, high-strength, and offer excellent mechanical properties. They are widely used in heat exchangers, condensers, evaporators, and transport pipelines.
Titanium seamless pipes
Outer diameter: 3.18mm - 50.8mm
Thickness: 0.6mm - 1.66mm
Materials: Gr.1, Gr.2, Gr.5, Gr.9, Gr.12, Gr.26, Gr.29
Contact us now

Titanium welded pipes
Outer diameter: 3.18mm - 38.1mm
Thickness:0.5mm - 50mm
Materials:Gr.1, Gr.2, Gr.3, Gr.5, Gr.7, Gr.9, Gr.12
Contact us nowTitanium threaded pipes
Types: Internal thread, external thread
Outer diameter: 6mm - 150mm
Thickness: 0.5mm - 15mm
Inner diameter: 6mm - 150mm
Contact us now

Titanium coil pipes
Outer diameter: 3mm - 914.40mm
Length:6000mm
Materials:Gr.1, Gr.2, Gr.3, Gr.4, Gr.5, Gr.7, Gr.9, Gr.12
Contact us nowBent titanium pipes
Outer diameter: 5mm - 114.3mm
Thickness: 0.5mm - 15mm
Cold bending process reduces welding work by over 80%.
Contact us now

Titanium reducer pipes
Titanium reducer pipes gradually change pipe diameter, ensuring smooth fluid transition under different flow and pressure conditions.
Contact us nowTitanium alloy thin-walled pipes
The high corrosion resistance of titanium alloys allows for thinner pipe designs, reducing space usage on ships and increasing layout flexibility.
Contact us now
Titanium fittings for marine applications
In the past, marine fittings were mainly made of copper, steel pipes, or stainless steel pipes with anti-corrosion coatings. However, their lifespan was relatively short.
By switching to titanium pumps, titanium valves, and titanium pipelines, the service life can be extended by 5 to 10 times. This not only significantly reduces overall costs but also ensures safe and reliable operation, preventing corrosion, leaks, and other safety hazards.
Titanium pumps
Titanium ensures pump stability and corrosion resistance in seawater environments, significantly extending service life.
Contact us now

Titanium valves
With high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, titanium valves operate reliably in highly corrosive environments.
Contact us nowTitanium flanges
Titanium flanges provide high strength and corrosion resistance, ensuring a secure and leak-proof system.
Contact us now

Titanium elbows
Elbows are pipe fittings used to change the direction of pipelines. The most common types include 45°, 90°, and 180° elbows.
Contact us now
Titanium caps

Titanium short pipe ends

Titanium reducers
Titanium plates for marine applications
Titanium plates are widely used in shipbuilding for hull structures, bulkheads, decks, propellers, cooling systems, and seawater pipelines.
With exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength, and lightweight properties, titanium plates enhance durability, reduce weight, and extend the service life of ships.
Contact us now
With exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength, and lightweight properties, titanium plates enhance durability, reduce weight, and extend the service life of ships.
- Thickness: 0.5mm - 120mm
- Width: 1000mm, 1200mm, 1500mm
- Length: 3000mm, 6000mm
- Grades: GR.1, GR.2, GR.3, GR.4, GR.5, GR.7, GR.12, GR.23
- Tolerance: As per specifications, industry standards, and custom requirements
- Flatness: 3mm per square meter
Titanium bars for marine applications
Titanium bars are primarily used in shipbuilding to manufacture high-strength, corrosion-resistant components such as propeller shafts, thrusters, valves, pumps, and fasteners.
With exceptional durability and reliability, titanium bars enhance vessel longevity, reduce maintenance costs, and extend service life.
Titanium round bar
Titanium round bars are widely used in ships for corrosion-resistant bearings, bolts, and other critical components.
Contact us now

Titanium square bar
Titanium square bars are commonly applied in ship structures and high-strength components.
Contact us nowTitanium flat bar
Titanium flat bars offer an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and durability, making them ideal for structural parts, fittings, and fasteners.
Contact us now

Titanium threaded bar
Titanium threaded bars are used to manufacture high-strength, corrosion-resistant connectors, ensuring secure fastening and sealing.
Contact us now- Grades: Grade 1, Grade 2, Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo, Ti-3Al-2.5V, Ti-5Al-2.5Sn
- Diameter: 6mm - 300mm
- Length: Customizable according to customer requirements
Marine structural transition joints
Structural transition joints enable the bonding of different metals while maintaining their original metallic properties.
These joints are also highly cost-effective, as they conserve rare metals and simplify the installation process.
Marine structural transition joints provide efficient, maintenance-free welded connections for titanium, steel, and aluminum structures in ships and offshore constructions.
Contact us now
We produce them in standard mother plates measuring 1300 x 3800 mm. Water jet cutting is used to create strips and other shapes from these plates.
Chalco Titanium offers the following specifications:
- Square
- Rectangular
- Disc
- Complex custom shapes
Titanium blocks for marine applications
Titanium blocks are widely used in ship hull structures, piping components, and precision equipment.
Their exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties enhance vessel durability and operational efficiency.
Titanium block specifications
Width: 300mm - 1500mm
Length: 200mm - 1400mm
Height: 20mm - 500mm
Grades: GR.1, GR.2, GR.5, GR.7, GR.9, GR.12
Contact us now
Marine fasteners
Marine titanium fasteners are widely used in various ship equipment and structures due to their excellent corrosion resistance and high strength. They ensure secure and reliable connections while extending the service life of components.

Titanium bolts

Titanium nuts

Titanium washers
Titanium alloy welding wires
Titanium alloy welding wires are widely used in shipbuilding, covering hull structures, propulsion systems, cooling systems, corrosion-resistant components, and onboard equipment.
Titanium welding ensures superior corrosion resistance, strength, and extended service life for ship components, making it an essential technology in modern ship manufacturing.

Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) welding wire

Ti-3Al-2.5V (Grade 12) welding wire

Pure titanium welding wire (Grade 1, Grade 2)
Why use titanium in ships?
- Lightweight and high strength: Titanium has only 57.7% of the density of steel but offers comparable strength. It can reduce ship weight by 40% while maintaining structural integrity, leading to lower fuel consumption.
- Exceptional corrosion resistance: Titanium is completely resistant to seawater corrosion and effectively withstands saltwater and aggressive fluids.
- Extended service life and low maintenance costs: Titanium lasts more than twice as long as steel or aluminum, significantly reducing maintenance expenses.
- Superior strength: Titanium alloys have the highest strength among marine metals in temperatures ranging from -253°C to 600°C.
- Heat resistance and thermal stability: Titanium withstands high temperatures, has a low thermal expansion coefficient, and experiences minimal welding deformation, making it safer for high-temperature ship components.
- Non-magnetic properties: Titanium prevents electromagnetic interference, enhancing the stealth capabilities of naval vessels.
- Excellent acoustic transparency: Titanium is an ideal material for sonar systems, fairings, and other acoustic equipment.
- Resistance to extreme environments: Titanium maintains high fracture toughness and fatigue strength in temperatures ranging from -60°C to 20°C, making it suitable for harsh marine conditions.
- Good machinability: Titanium can be processed using various methods, including casting, rolling, forging, and extrusion, making it adaptable for different ship structures.
- High recycling value: Compared to steel, titanium scrap has a significantly higher recovery value.
Cost control recommendations for titanium applications in ships
Selecting the right alloy, form, and manufacturing process to produce efficient and cost-effective components and systems is more important than simply using low-cost materials.
Directly replacing steel or other alloys with titanium on a one-to-one basis can be costly and may lead to titanium being abandoned in certain applications.
Redesigning with the following principles will yield significant benefits:
- Avoid simply substituting titanium into existing designs.
- Do not estimate titanium project costs based on weight, especially not using the weight of steel or copper alloy components as a reference.
- Review standard products and specifications to achieve the best availability and lowest cost.
- Use a design strategy based on minimal material thickness.
- Fully leverage titanium’s corrosion resistance.
- For piping, use cold bending or induction bending to minimize the need for elbows, flanges, and welding.
- Refer to flange guidelines to determine the lowest-cost system that meets design specifications.
- For heavy components, consider composite layers instead of solid designs.
- For castings such as valves and pumps, if the quantity is sufficient, develop new patterns to optimize titanium’s strength and corrosion resistance.
- Consult suppliers and manufacturers at the earliest design stage.
Pioneering the use of titanium will help shipyards stand out in a competitive market and gain a strategic advantage.Quick Quote
Corrosion performance of titanium alloys in natural and polluted seawater compared to other metals
| Mode of Corrosion | Copper based alloys | Stainless Steel 316 | Stainless Steel 6 Mo and Duplex | Titanium Alloys |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Corrosion | Resistant/Susceptible | Resistant | Resistant | Resistant |
| Crevice Corrosion | Susceptible | Susceptible | Susceptible (>25°C) | Resistant (<80°c) |
| Pitting Attack | Susceptible | Susceptible | Resistant | Immune |
| Stress Corrosion | Susceptible | Susceptible (>60°C) | Resistant | Resistant |
| Corrosion Fatigue | Susceptible | Susceptible | Susceptible | Immune |
| Galvanic attack | Susceptible | Susceptible | Resistant | Immune |
| Microbiological Corrosion (MIC) | Susceptible | Susceptible | Susceptible | Immune |
| Weld/HAZ Corrosion | Susceptible | Susceptible | Susceptible | Resistant |
| Erosion Corrosion | Susceptible | Resistant | Resistant | Highly Resistant |

Marine titanium is not difficult to weld
Titanium welding is not complicated, and multiple welding techniques are available, including Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (TIG), Electron Beam Welding, Laser Welding, and Friction Stir Welding (FSW).
The best welding method is usually chosen based on structural configuration, joint design, performance requirements, and cost considerations.
Although titanium welding technology is well-established, traditional welding methods can be slow for shipbuilding projects that require long weld seams.
To address this, we have developed a friction stir welding (FSW) technique specifically for titanium alloys. This method softens rather than melts the adjacent metal sheets, efficiently joining titanium plates over 70 feet long.
After welding, all joints undergo thorough inspection to ensure the highest quality standards.

Why choose us
- Technical expertise: We have a leading edge in machining, bending, and welding of titanium materials, especially in thin-walled titanium pipe cold bending technology.
- Competitive pricing: We offer cost-effective pricing for distributors, ensuring a profitable margin for our customers.
- Customization capability: We provide customized titanium products with special specifications and grades based on customer requirements.
- Product quality and certification: Our products strictly comply with international quality standards and come with the necessary certification documents.
- Tariff estimation: We help customers anticipate potential tariffs and plan accordingly.
- Stable supply capacity: With strong production capabilities and a well-managed supply chain, we ensure on-time delivery.
- Flexible cooperation: We strive to establish long-term and stable partnerships with our clients.
- Technical support and solutions: In addition to high-quality titanium products, we provide technical consultation for end customers.
- Reliable after-sales service: We offer comprehensive after-sales support, ensuring a seamless purchasing and usage experience.
Packaging and transportation of marine titanium materials
To ensure that titanium materials remain undamaged during transportation, we provide professional packaging and shipping services. Here are our advantages in this area:
- Professional packaging: We offer customized packaging solutions for marine titanium materials. Depending on the size and shape, we use special wooden crates, steel banding, bubble wrap, and multiple protective measures to ensure safety.
- Shipping options: We cooperate with multiple logistics providers and offer sea, air, and land transportation to select the most suitable shipping method based on customer needs.
- Real-time tracking and updates: Throughout the shipping process, we provide real-time logistics tracking, allowing customers to monitor their shipment status at any time.
- Global delivery capability: With a worldwide shipping network, we ensure efficient and secure delivery of titanium materials to customers in any country or region.
Frequently asked questions
Does titanium alloy require additional anti-corrosion treatment?
Titanium alloys have excellent corrosion resistance, especially in seawater environments, and do not require additional anti-corrosion treatment. Unlike steel, titanium alloys do not need regular painting or protective coatings, reducing maintenance workload and costs.
How strong are titanium alloys? Can they withstand high pressure and impact?
Titanium alloys, especially high-strength alloys like Ti-6Al-4V, offer exceptional strength and fatigue resistance. They remain stable even under high-pressure and impact conditions.
How does titanium compare to steel in shipbuilding?
Titanium has superior corrosion resistance, which is crucial in harsh marine environments.
Titanium is 43% lighter than steel while maintaining comparable strength. This helps reduce ship weight without compromising structural integrity.
Titanium can withstand higher temperatures and has better fatigue strength, making it ideal for components exposed to cyclic stress.
Titanium is non-magnetic, a critical feature for stealth applications in nuclear submarines and other military vessels.
What are the cost benefits of using titanium alloys compared to traditional materials?
Although the initial cost of titanium alloys is higher, they provide long-term cost benefits in shipbuilding.
High strength, low density, and corrosion resistance make titanium a smart long-term investment.
Titanium extends the lifespan of ships and reduces maintenance costs, offsetting the higher upfront investment.
Why is titanium used in heat exchangers?
Seawater is highly corrosive and erosive, causing limited lifespans for copper and stainless steel heat exchangers.
Any leakage in a heat exchanger can flood machinery with seawater, leading to catastrophic failures.
Titanium is completely unaffected by seawater and, with proper maintenance, can last many years without degradation.
What are the benefits of using titanium for water-cooled exhaust systems?
If wet exhaust system components are made from stainless steel or copper, they are vulnerable to corrosion from acidic compounds in the hot exhaust flow.
Titanium exhaust systems have a much longer lifespan. They are resistant to acidic gases and high-temperature exhaust (up to 1200°C), preventing costly downtime and failures.